Chandrayaan 3, India’s third lunar exploration mission under the ISRO. It carries two main components a lander named Vikram and a Rover named Pragyan, similar to the Chandrayaan-2.
Chandrayaan 3 was launched on 14 July 2023 by LVM3 Rocket.LVM3 is the operational heavy-lift launch vehicle of ISRO and has a spectacular pedigree of completing 6 consecutive successful missions. This is the 4th operational flight of LVM3, which aims to launch the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft to Geo Transfer Orbit (GTO).
What is LVM3 Rocket?
The LVM3 (Launch Vehicle Mark 3) is a rocket developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the space agency of India. It is designed to launch satellites into orbit and has a payload capacity of up to 4 tons for geostationary transfer orbit missions. The LVM3 is a three-stage rocket, with the core stage and strap-on boosters using solid propellant, while the upper stage uses liquid propellant. It has been used for various missions, including the launch of India’s Chandrayaan-2 lunar mission in 2019.
The lander along with the rover landed on the south pole of the moon on 23 August 2023. At 6:02, this was the moment when India became the first country to land on the South Pole and the fourth country to make a soft landing on the moon’s surface.
This moon mission was proposed on the failure of Chandrayaan-2. ISRO launched Chandrayaan-2 on 22 July 2019 and in September 2019. lander had to touch the surface but it deviated from its path and crashed.
 LVM3
LVM3
ISRO Set the Following Mission Objectives for the Chandrayaan-3 Mission:
- Getting a lander to land safely and softly on the surface of the Moon.
- Observation of the rover’s driving capabilities on the Moon.
- Conducting experiments on the materials available on the moon’s surface to better understand the composition of the Moon.
Related Article: PM (Vishwakarma) Shram Kaushal Samman Yojana 2023
Chandrayaan-3 Consists of Three Main Components:
Propulsion module
This module carries the lander and Hover to 100 km in moon orbit. Its main function is to carry the Land module from the launch vehicle injection orbit to the Lander separation.
Major Specification of Propulsion Module:
This module’s life is carrying LM and Rover to moon orbit and completing the experimental target in a period of 3 to 6 months. Its Power Generation is 738w, Summer Solstice, and with biased communication. system, S-Band Indhsponder -with IDSN.
Payload of Propulsion Module
To study the (SHAPE) Spectropolarimetric sign of the habitable planet Earth in the near-infrared wavelength range.
What is Lander
Lander who is responsible for the soft landing on the moon is Viknam. It carries the rover and various scientific instruments to perform on-site analysis.
Major Specification of Lander
This Lander life is 1 lunar day (14 Earth days). Its power is 738 w (winter solstice)and it has communication with ISDN, Ch-2 onballer, and Rover. Lander has 3 payloads.
Payloads of Lander
1. RAMBHA-LP
To measure the near-surface (Langmuir Probe) plasma (ions and electrons) density and changes with time.
2. ChaSTE
To study on measure the thermal properties of the moon’s surface near the south pole
3. ILSA
To measure seismic around.
the landing site and delineating the structure of the moon’s crust and mantle.
 Lander
Lander
What is Rover
A rover named Pragyan has a six-wheeled vehicle. This moves on the surface and makes major experiments like the presence of water ice, the history of lunar impacts, and the atmosphere of the moon.
Major specifications of Rover
This Rover’s life is 1 Lunar day. Its power is 50W and has a communication system, Lander. It has 2 payloads.
Payloads of Rover
1. APXS
To know the chemical composition. for further understanding of the moon’s surface.
2. LIBS
To detect the elemental composition of moon soil and rocks.
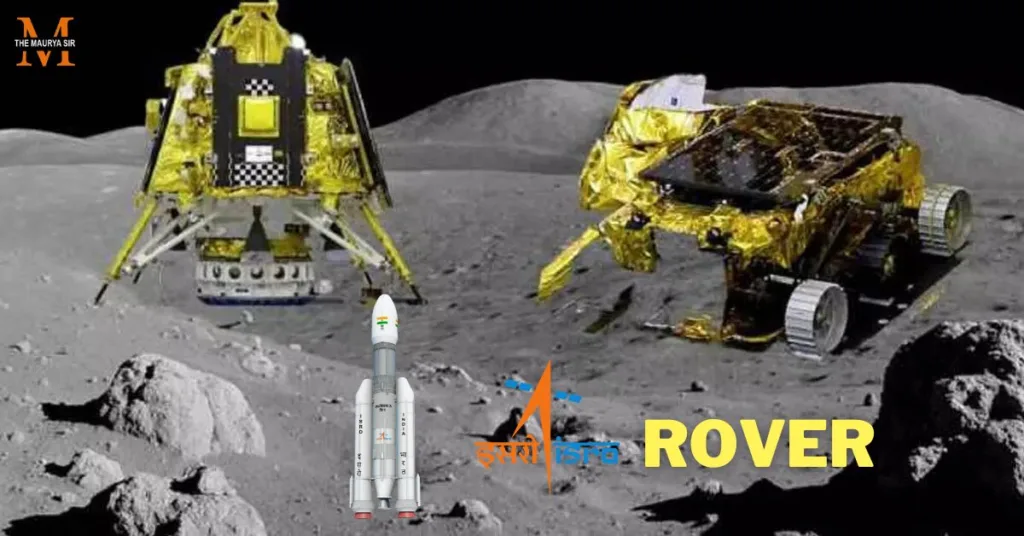 Rover
Rover
The Chandrayaan 3 mission was successful because of the teamwork of the scientists of ISRO. The Prime Minister of India Shri Narendra Modi congratulated the ISRO team and the whole of India.
ISRO Chairperson: S. Somanath.
Mission Director: S. Mohanakumar.
Associate Mission Director: G. Narayanan.
Project Director: P. Veeramuthuvel.
Deputy Project Director: Kalpana. K.
Vehicle Director: Biju C. Thomas.
What is the Next Mission of ISRO?
ISRO Further Mission will be :
Aditya -L1 is the first Indian mission dedicated to observing the sun and is planned to be launched aboard a PSLV-XL Jaunch vehicle in September 2023, 6 Years (Real Date Not Confirm) ISRO at Satish Dhawan Space Centre!
Its main objectives are coronal heatings, solar wind acceleration, coronal magnetometry for observation of photo sphex, chromosphere! and corona, and magnetic field of the sun.
Another Mission Planned by ISRO Chairperson S. Somanath is:
Venus Orbiter Mission, unofficially known as Shukrayaan is planned to be launched in December 2023 (Real date not confirmed) by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) mission to study the surface and atmosphere of Venus.
FAQs
What is Venus Orbiter Mission?
Venus Orbiter Mission, unofficially known as Shukrayaan is planned to be launched in December 2023 (Real date not confirmed) by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) mission to study the surface and atmosphere of Venus.
What is Aditya -L1 Mission?
Aditya -L1 is the first Indian mission dedicated to observing the sun and is planned to be launched aboard a PSLV-XL Jaunch vehicle in September 2023, 6 Years (Real Date Not Confirm) ISRO at Satish Dhawan Space Centre!
What is the Next Mission of ISRO in 2023?
The ISRO’s next mission is Aditya – L1 for SUN, and Venus Orbiter Mission for Venus.
